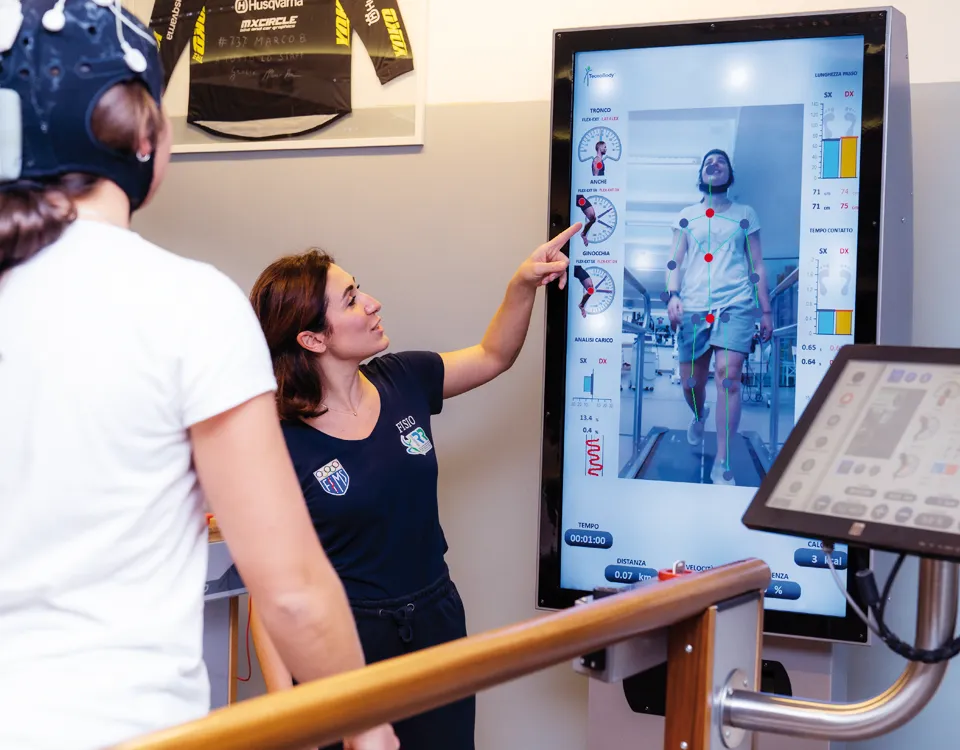
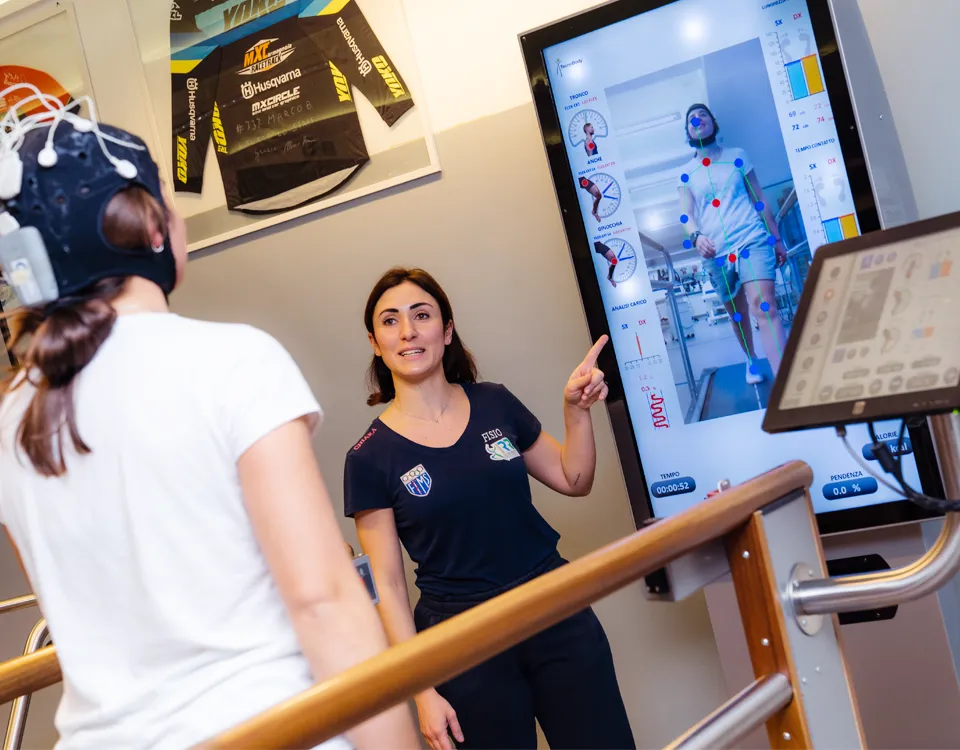
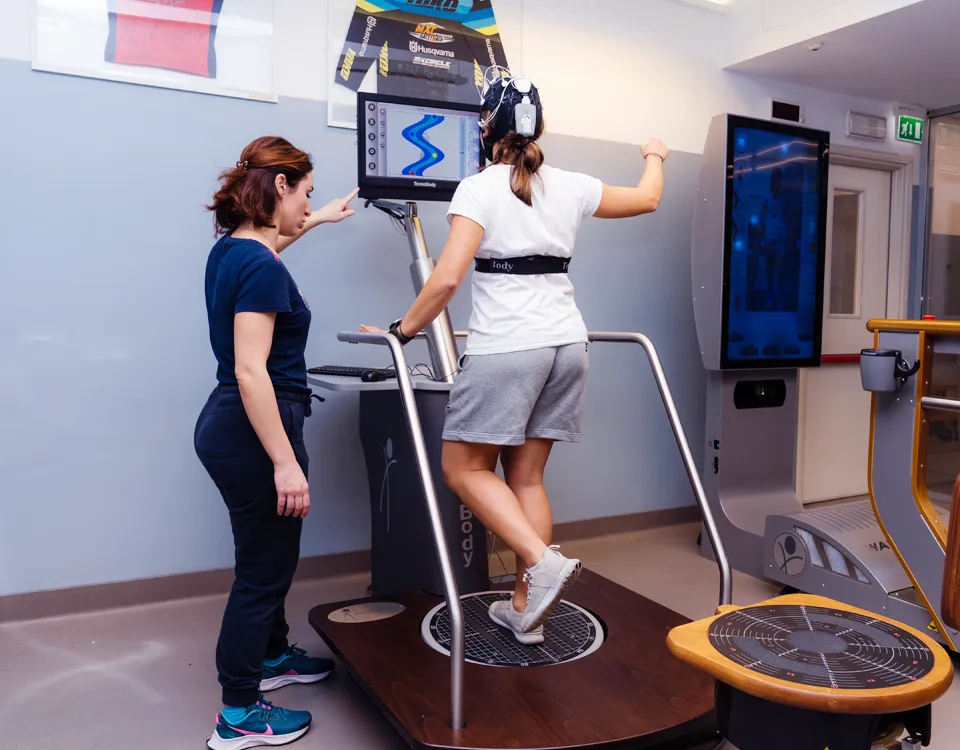
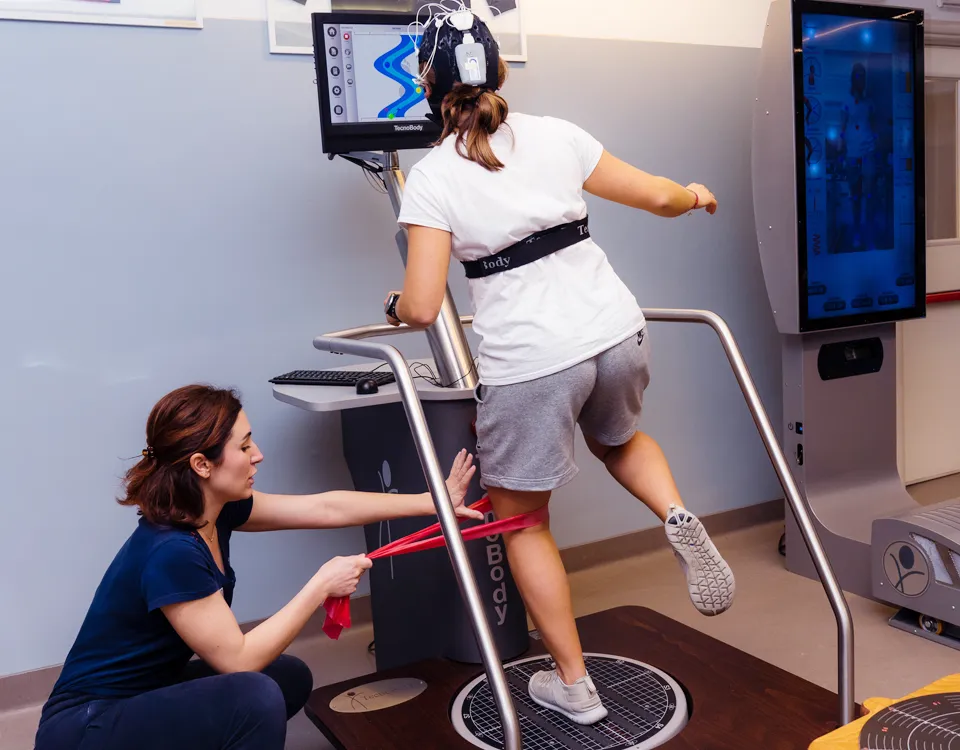
The IRR Rehabilitations Institute opening hours: from Monday to Friday from 8:00 to 20:00
- The Group
- Phisioterapy
Rehabilitation areas
- Sports medicine
Sports Medicine Institute
- Diagnostic
Visits
Learn about all of the center’s specialist visits
- Technologies
- Alter g
- Hyperthermia
- Isokinetics
- Kinesis
- Leap motion device
- Opaf
- Quark pft
- Reflexion rehabilitative measurement tool
- Riablo
- Stabilometric platform
- Transcranial electrical stimulation
- Vibra
- Walker view
Technologies